Barwon Water is launching a key initiative, Building a Resilient Barham, to protect water quality and environmental resilience in the Barham River Catchment. This long-term project takes a whole-of-catchment management approach to mitigate public health risks while delivering broader environmental and landholder benefits.
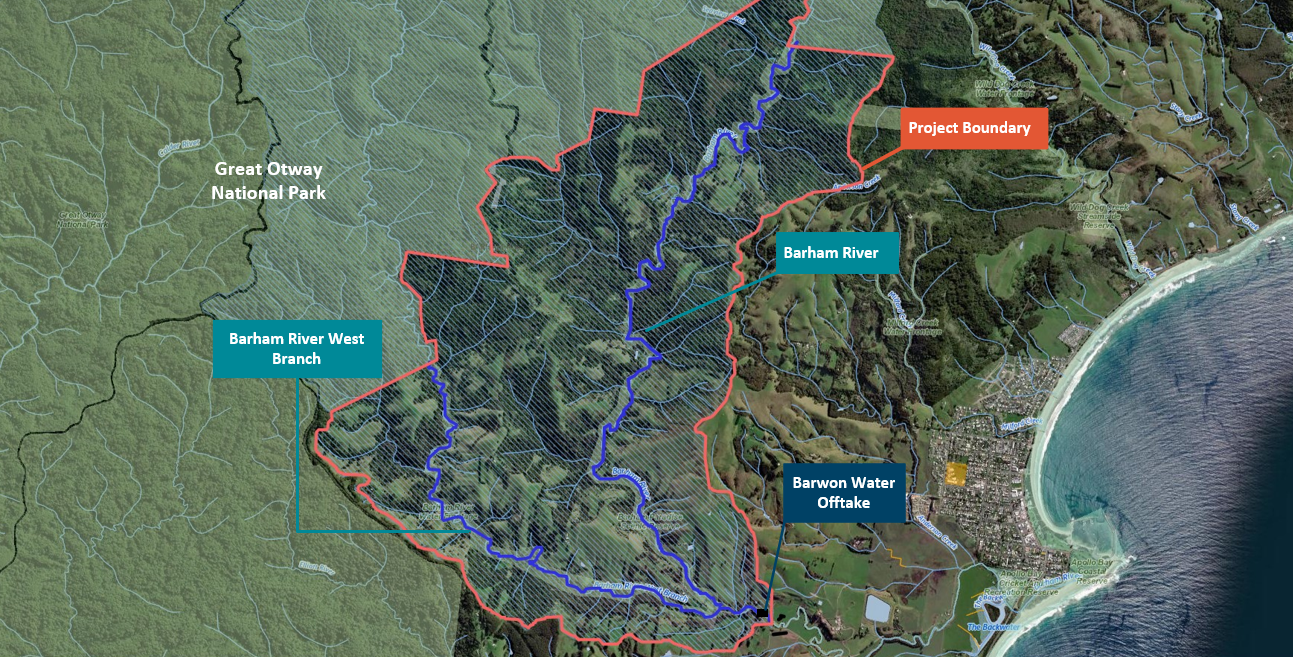
Access to safe drinking water depends on effective catchment management and water quality protection. The Barham River Catchment supplies drinking water to Apollo Bay, Marengo, and Skenes Creek. Water is drawn from the Barham River Pump Station, located approximately 400 meters downstream of the confluence of the Barham River and its west branch. However, as the river flows downstream, it is exposed to multiple risks, including livestock access to waterways, paddock runoff, and failing domestic septic systems.
In compliance with the Safe Drinking Water Act and Regulations, Barwon Water implements a multi-barrier approach to safeguard water quality. A key component of this approach is conducting regular Catchment Risk Assessments to identify and manage potential threats to drinking water.
Whilst the Apollo Bay Water Treatment Plant is currently able to produce safe drinking water, the implementation of whole-of-catchment management and waterway protection works will prevent and minimise the contamination of the river and its major tributaries and increase confidence in the treatment of future water quality risks.
Through Building a Resilient Barham, Barwon Water is committed to proactive risk management and collaborative catchment stewardship, ensuring the long-term sustainability of this vital water source.
What does the project involve?
Building a Resilient Barham will deliver a 30-year catchment management approach involving on-ground waterway protection works, community engagement and monitoring and evaluation.
We’ll be engaging and collaborating with local landowners and community groups to implement:
- Revegetation and weed management along the Barham River and its tributaries,
- Fencing to limit stock access to waterways,
- Septic system assessments with maintenance advice and potential support for necessary repairs,
- Long-term monitoring of water quality and vegetation.
The benefits for landholders, their property and the environment include:
- Expert guidance – To plan, implement and maintain tailored waterway protection works for your property.
- Financial assistance - To implement and maintain tailored waterway protection works.
- Ongoing weed control – We will support continued weed management in revegetated areas.
- Septic system support – If your system is failing, funding may be available for repairs or replacement.
- Improved stock protection – Once mature, revegetated areas provide shelter from harsh weather.
- Reduced erosion and flood damage – Fencing and native vegetation help stabilize banks and minimize property damage.
- Lower risk of stock injury – Keeping animals away from waterways prevents drowning and other hazards.
- Reduced fire risk - Well manage streamside vegetation is less likely to contribute to the spread of fire than pasture or crops.
- Increased habitat – Revegetation will support diverse communities of water dependent plants and animals.
- Increased native vegetation - As coverage increases, native vegetation will filter and buffer the waterways from pollutants.
Map
Glossary
| Off Stream Watering | Off stream watering occurs when groundwater (from a spring, well or aquifer) or surface water, such as a river or stream, is diverted from its source to a water trough or tank for domestic stock to drink. |
| Pathogen | Any small organism, such as a virus or bacterium that can cause disease. E.g. E.coli, Salmonella spp., Shingella spp. |
| Revegetation | Revegetation is the process of replanting of disturbed land. It can occur naturally through plant colonization and succession, or it can be accelerated through human-driven efforts to repair damage. |
| Riparian | Refers to the area of land alongside a river such as riverbanks, flood plains, wetlands or vegetation |
| Siltation | Siltation is a process or type of soil erosion. Siltation can block or fill waterways as fine soil erodes and builds up. |
| Turbidity | Turbidity refers to the cloudiness or haziness of a fluid. In a waterway, turbidity can be caused by erosion and an increase in fine soil particles suspended in the water. |
| Water Protection Practices | The evolving practice of safeguarding the quality of water through solutions like revegetation, vegetation buffers and fencing. |





